High platelet count is often referred to as 'platelet count' because it is measured using platelets. Platelets serve to repair blood clots that have formed inside the arteries, by sticking to the surfaces of injured arterial walls. They then clump together or aggregate into clotted platelets, ready for coagulation when they are broken down by the liver. A healthy platelet count usually ranges between 200,000 and 300,000.
Platelets are formed in the bone marrow, removed from the bone and then broken down into smaller pieces. There are two types of platelets: large and small.
Platelets that are large are called mononuclear platelets. They can be broken down into larger particles when they encounter the fibrin coating on blood cells. The fibrin molecules attach themselves to the platelets, which then start to fibrillate. Fibrin bonds with other platelets forming aggregates.
Small platelets are also called fibrinogen, and they are smaller than mononuclear platelets. They are generally made up of about ten percent fibrin. The fibrin bonds with mononuclear platelets, which will help them to be broken down and released into the blood. However, there are some people who do not produce enough fibrin, making these platelets too dense to be useful for making coagulated blood clots.
When blood clot breaks loose from an artery, a new plot is created by the body, and it is then broken apart by clotting mechanisms. Fibrin can be drawn into the body from the clot by an artery-clogging blood vessel. This can be done by the clot's sticky back or the blood vessel's thin wall, or even the clot's hardening. onto itself, forming a clot.
The clot is pulled into the blood through the blood by a clotting enzyme that is part of the body's immune system. If this process is blocked, the clot sticks to the wall of the blood vessel, which can't be pulled any further into the bloodstream. If this happens, it becomes a potential blockage. and the clot clots, or fibrin fragments will need to be removed from the artery.
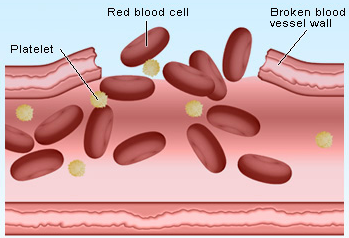
High platelets can also be produced by the body if there is an infection. The infection itself can kill or disable the infection-fighting bacteria in the blood, but the production of high platelets helps to keep the bacteria in check so that the infection cannot grow. The bacteria help by producing additional platelets.
High platelets are usually needed to prevent any clot from growing too big to be removed from the artery and becoming blockage
If there is an obstruction, a physician can remove the clot with a simple procedure, but it may take more complicated surgery to get rid of the blockage.
Platelets also help with keeping blood circulating through the body. When the heart is pumping at a high rate, there is less clotting. Platelets, together with other white blood cells, help the heart pump by sending the right signals to the body's white blood cells. As the body's white blood cells to fight infection and reduce inflammation, the amount of clotting reduces as well.
Platelets are also necessary for wound healing. The amount of clotting that occurs when there is an injury varies based on the severity of the injury. Platelet count drops dramatically in severe cases, and platelet count increases after the wound heals. This helps to speed the healing time.
Even in cases where low platelet count does not have any negative effect, it is still possible for a low platelet count to be unhealthy. If a person has chronic low platelet count, they should consult a doctor. A person with chronic low platelet count might be more likely to develop a type of arthritis known as osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis occurs because the body's natural defenses are worn out and it causes the joint's cartilage to wear away, making the joint vulnerable.
Osteoarthritis can cause the pain and swelling that people with it experience. In addition to the pain, the joint can be sensitive to touch, and sometimes it also affects the blood vessels in the knee. When left untreated, osteoarthritis can progress into a type of arthritis known as rheumatoid arthritis.